10.54 KSEXT—A canonical kick sextupole, which differs from the MULT element with ORDER=2
in that it can be used for chromaticity correction.
A canonical kick sextupole, which differs from the MULT element with ORDER=2 in that it can be used
for chromaticity correction.
Parallel capable? : yes
GPU capable? : yes
Back-tracking capable? : yes
|
|
|
|
|
| Parameter Name | Units | Type | Default | Description |
|
|
|
|
|
| L | M | double | 0.0 | length |
|
|
|
|
|
| K2 | 1∕M3 | double | 0.0 | geometric strength |
|
|
|
|
|
| K1 | 1∕M2 | double | 0.0 | geometric quadrupole strength
error. See notes below! |
|
|
|
|
|
| J1 | 1∕M2 | double | 0.0 | geometric skew
quadrupole strength error. See
notes below! |
|
|
|
|
|
| TILT | RAD | double | 0.0 | rotation about longitudinal
axis |
|
|
|
|
|
| PITCH | RAD | double | 0.0 | rotation
about horizontal axis. Ignored
if MALIGN_METHOD=0 |
|
|
|
|
|
| YAW | RAD | double | 0.0 | rotation
about vertical axis. Ignored if
MALIGN_METHOD=0 |
|
|
|
|
|
| BORE | M | double | 0.0 | bore radius |
|
|
|
|
|
| B | T | double | 0.0 | field at pole tip (used if bore
nonzero) |
|
|
|
|
|
| N_KICKS | | long | 0 | number of kicks (rounded up
to next multipole of 4 if
INTEGRATION_ORDER=4.
Deprecated. Use N_SLICES.) |
|
|
|
|
|
| N_SLICES | | long | 1 | Number of slices (full
integrator steps). |
|
|
|
|
|
| DX | M | double | 0.0 | misalignment |
|
|
|
|
|
| DY | M | double | 0.0 | misalignment |
|
|
|
|
|
| DZ | M | double | 0.0 | misalignment |
|
|
|
|
|
| FSE | | double | 0.0 | fractional strength error |
|
|
|
|
|
| HKICK | RAD | double | 0.0 | horizontal correction kick |
|
|
|
|
|
| VKICK | RAD | double | 0.0 | vertical correction kick |
|
|
|
|
|
| HCALIBRATION | | double | 1 | calibration factor for
horizontal correction kick |
|
|
|
|
|
| VCALIBRATION | | double | 1 | calibration factor for vertical
correction kick |
|
|
|
|
|
| HSTEERING | | short | 0 | use for horizontal correction? |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
A canonical kick sextupole, which differs from the MULT element with ORDER=2 in that it can be used for
chromaticity correction.
|
|
|
|
|
| Parameter Name | Units | Type | Default | Description |
|
|
|
|
|
| VSTEERING | | short | 0 | use for vertical correction? |
|
|
|
|
|
| SYNCH_RAD | | short | 0 | include classical,
single-particle synchrotron
radiation? |
|
|
|
|
|
| SYSTEMATIC_MULTIPOLES | | STRING | NULL | input file for systematic
multipoles |
|
|
|
|
|
| EDGE_MULTIPOLES | | STRING | NULL | input file for systematic edge
multipoles |
|
|
|
|
|
| RANDOM_MULTIPOLES | | STRING | NULL | input file for random
multipoles |
|
|
|
|
|
| STEERING_MULTIPOLES | | STRING | NULL | input file for multipole content
of steering kicks |
|
|
|
|
|
| SYSTEMATIC_MULTIPOLE_FACTOR | | double | 1 | Factor by which to
multiply systematic and edge
multipoles |
|
|
|
|
|
| RANDOM_MULTIPOLE_FACTOR | | double | 1 | Factor by which to multiply
random multipoles |
|
|
|
|
|
| STEERING_MULTIPOLE_FACTOR | | double | 1 | Factor by which to multiply
steering multipoles |
|
|
|
|
|
| MIN_NORMAL_ORDER | | short | -1 | If nonnegative,
minimum order of systematic
and random normal multipoles
to use from data files. |
|
|
|
|
|
| MIN_SKEW_ORDER | | short | -1 | If nonnegative,
minimum order of systematic
and random skew multipoles
to use from data files. |
|
|
|
|
|
| MAX_NORMAL_ORDER | | short | -1 | If nonnegative,
maximum order of systematic
and random normal multipoles
to use from data files. |
|
|
|
|
|
| MAX_SKEW_ORDER | | short | -1 | If nonnegative,
maximum order of systematic
and random skew multipoles
to use from data files. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
A canonical kick sextupole, which differs from the MULT element with ORDER=2 in that it can be used for
chromaticity correction.
|
|
|
|
|
| Parameter Name | Units | Type | Default | Description |
|
|
|
|
|
| INTEGRATION_ORDER | | short | 4 | integration order (2, 4, or 6) |
|
|
|
|
|
| SQRT_ORDER | | short | 0 | Ignored, kept for backward
compatibility only. |
|
|
|
|
|
| ISR | | short | 0 | include incoherent
synchrotron radiation
(quantum excitation)? |
|
|
|
|
|
| ISR1PART | | short | 1 | Include ISR for single-particle
beam only if ISR=1 and
ISR1PART=1 |
|
|
|
|
|
| EXPAND_HAMILTONIAN | | short | 0 | If 1, Hamiltonian is expanded
to leading order. |
|
|
|
|
|
| MALIGN_METHOD | | short | 0 | 0=original, 1=new
entrace-centered, 2=new
body-centered |
|
|
|
|
|
| GROUP | | string | NULL | Optionally used to assign an
element to a group, with
a user-defined name. Group
names will appear in the
parameter output file in the
column ElementGroup |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
This element simulates a sextupole using a kick method based on symplectic integration. The user
specifies the number of kicks and the order of the integration. For computation of twiss parameters,
chromaticities, and response matrices, this element is treated like a standard thick-lens sextuupole; i.e.,
the number of kicks and the integration order become irrelevant.
Multipole errors
Specification of systematic and random multipole errors is supported through the SYSTEMATIC_MULTIPOLES,
EDGE_MULTIPOLES, and RANDOM_MULTIPOLES fields. These specify, respectively, fixed multipole strengths
for the body of the element, fixed multipole strengths for the edges of the element, and random multipole
strengths for the body of the element. These fields give the names of SDDS files that supply the multipole
data. The files are expected to contain a single page of data with the following elements:
- Floating point parameter referenceRadius giving the reference radius for the multipole data.
- An integer column named order giving the order of the multipole. The order is defined as
(Npoles - 2)∕2, so a quadrupole has order 1, a sextupole has order 2, and so on.
- Floating point columns normal and skew giving the values for the normal and skew multipole
strengths, respectively. (N.B.: previous versions used the names an and bn, respectively. This
is still accepted but deprecated) These are defined as a fraction of the main field strength
measured at the reference radius, R: fn =
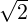 , where m = 2 is the order of the main field
and n is the order of the error multipole. A similar relationship holds for the skew multipole
fractional strengths. For random multipoles, the values are interpreted as rms values for the
distribution.
, where m = 2 is the order of the main field
and n is the order of the error multipole. A similar relationship holds for the skew multipole
fractional strengths. For random multipoles, the values are interpreted as rms values for the
distribution.
Specification of systematic higher multipoles due to steering fields is supported through the
STEERING_MULTIPOLES field. This field gives the name of an SDDS file that supplies the multipole data.
The file is expected to contain a single page of data with the following elements:
- Floating point parameter referenceRadius giving the reference radius for the multipole data.
- An integer column named order giving the order of the multipole. The order is defined as
(Npoles - 2)∕2. The order must be an even number because of the quadrupole symmetry.
- Floating point column normal giving the values for the normal multipole strengths, which are
driven by the horizontal steering field. (N.B.: previous versions used the name an for this data.
This is still accepted but deprecated) normal is specifies the multipole strength as a fraction
fn of the steering field strength measured at the reference radius, R: fn =
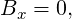 , where
m = 0 is the order of the steering field and n is the order of the error multipole. The skew values
(for vertical steering) are deduced from the normal values, specifically, gn = fn * (-1)n∕2.
, where
m = 0 is the order of the steering field and n is the order of the error multipole. The skew values
(for vertical steering) are deduced from the normal values, specifically, gn = fn * (-1)n∕2.
Another way of introducing errors is via the K1 and J1 parameters, which allow introducing a normal
and skew quadrupole error term. For tracking, the strength of these values can be arbitrarily high
without introducing errors. However, the matrix analysis (e.g., for determination of tunes and beta
functions) assumes that these are weak effects and high accuracy should not be expected if this is not
true. If K1 is significant, then use of the KQUSE element is preferred.
Apertures
Apertures specified via an upstream MAXAMP element or an aperture_input command will be imposed
inside this element.
Misalignments
There are three modes for implementing alignment errors. Which is used is controlled by the value of
the MALIGN_METHOD parameter:
- MALIGN_METHOD=0 — This selects the original method, which was the only one available before
version 2021.1. The misalignment is referenced to the entrance face. The YAW and PITCH
parameters are ignored.
- MALIGN_METHOD=1 — This selects a linearized method based on M. Venturini’s work [58],
with misalignment referenced to the entrance face. The YAW and PITCH parameters are
implemented.
- MALIGN_METHOD=2 — This selects a linearized method based on M. Venturini’s work [58],
with misalignment referenced to the magnet center. The YAW and PITCH parameters are
implemented.
- MALIGN_METHOD=3 — This selects an exact method based on M. Venturini’s work [58],
with misalignment referenced to the entrance face. The YAW and PITCH parameters are
implemented.
- MALIGN_METHOD=4 — This selects an exact method based on M. Venturini’s work [58],
with misalignment referenced to the magnet center. The YAW and PITCH parameters are
implemented.
For elements with non-zero TILT, error displacements and rotations are performed in the lab
frame.
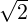 , where m = 2 is the order of the main field
and n is the order of the error multipole. A similar relationship holds for the skew multipole
fractional strengths. For random multipoles, the values are interpreted as rms values for the
distribution.
, where m = 2 is the order of the main field
and n is the order of the error multipole. A similar relationship holds for the skew multipole
fractional strengths. For random multipoles, the values are interpreted as rms values for the
distribution.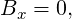 , where
, where